Low Carb Diet for Diabetics
Living with diabetes requires careful attention to one’s diet to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Among the various dietary approaches available, a low carb diet has gained considerable attention for its potential to help diabetics improve their health and maintain stable blood sugar levels. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and guidelines of a low carb diet for diabetics.
The Role of a Low Carb Diet in Diabetes Management
A low carb diet has gained significant attention as an effective approach for managing diabetes. It involves reducing the consumption of carbohydrates and replacing them with healthier alternatives. This dietary strategy has shown promising results in helping individuals with diabetes control their blood sugar levels and improve overall health. In this blog post, we will explore the role of a low carb diet in diabetes management.
Understanding a Low Carb Diet
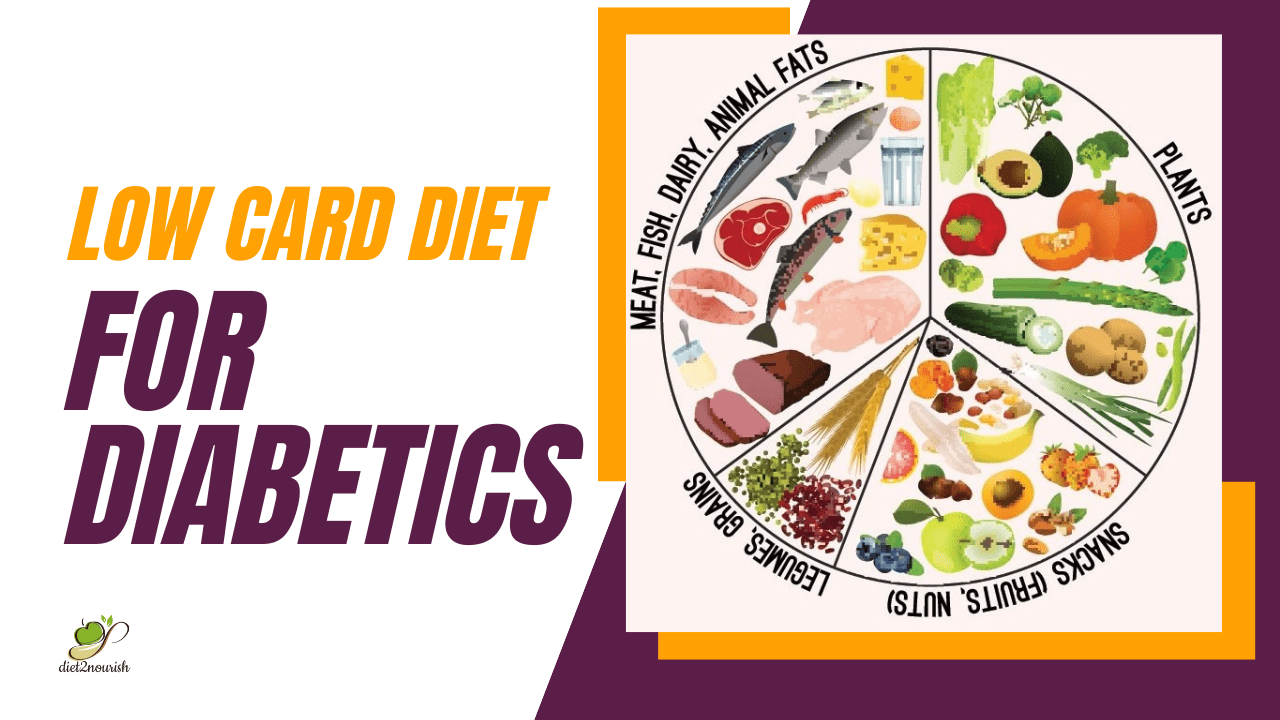
A low carb diet focuses on reducing the intake of carbohydrates, particularly refined and processed carbs, such as white bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and sugary beverages. Instead, the emphasis is on consuming foods that are high in protein, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables. This dietary approach aims to minimize blood sugar spikes and promote stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Benefits of a Low Carb Diet for Diabetes Management:
1. Improved Blood Sugar Control:
One of the primary benefits of a low carb diet for diabetics is better blood sugar control. Carbohydrates are the main macronutrient that significantly affects blood sugar levels. By reducing carbohydrate intake, individuals can minimize blood sugar spikes, leading to better glycemic control and reducing the need for medication.
2. Weight Management:
Obesity and excess weight are common risk factors for type 2 diabetes and can exacerbate insulin resistance. A low carb diet can be effective for weight management as it encourages the consumption of satiating proteins and healthy fats, which can help reduce calorie intake and promote weight loss. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for diabetes management.
3. Lowered Insulin Requirements:
With improved blood sugar control and weight management, many diabetics find that their insulin requirements decrease when following a low carb diet. This reduction in insulin dependence can lead to fewer injections or lower medication dosages, making diabetes management more convenient and cost-effective.
4. Improved Cardiovascular Health:
Diabetes increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Following a low carb diet can help improve cardiovascular health markers, such as reducing triglyceride levels, increasing HDL (good) cholesterol, and lowering blood pressure. These benefits can contribute to a lower risk of heart disease, which is common in individuals with diabetes.
5. Increased Energy Levels and Mental Clarity:
Many diabetics report experiencing increased energy levels and improved mental clarity when following a low carb diet. By avoiding blood sugar spikes and crashes associated with high carb meals, diabetics can maintain a steady supply of energy throughout the day, reducing fatigue and improving cognitive function.
Implementing a Low Carb Diet for Diabetes Management:
It’s important to note that a low carb diet should be approached with guidance from a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide individualized advice. Here are some general guidelines to consider:
1. Limit Carbohydrate Intake:
Reduce the consumption of refined carbohydrates and sugary foods and beverages. Instead, choose whole foods that are low in carbs, such as non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2. Choose Healthy Sources of Protein and Fat:
Include lean sources of protein like poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, and legumes. Incorporate healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. These provide essential nutrients and contribute to satiety.
3. Focus on Non-Starchy Vegetables:
Non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, and zucchini are low in carbs and high in fiber and essential nutrients. They can be enjoyed in abundance on a low carb diet.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels:
Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to understand how different foods and portion sizes affect your body. This will help you make informed decisions about your diet and adjust your medication as necessary.
What is a Low Carb Diet?
A low carb diet involves reducing the consumption of carbohydrates and replacing them with healthier alternatives. Typically, this means limiting or avoiding foods such as bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and sugary beverages. Instead, the focus is on consuming foods that are high in protein, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables.
Guidelines of a Low Carb Diet for Diabetics
A low carb diet can be an effective strategy for managing diabetes and controlling blood sugar levels. However, it’s important to approach this dietary approach with proper guidelines and individualized advice from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians. Here are some general guidelines to consider when adopting a low carb diet for diabetes management.
1. Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
Before making any significant changes to your diet, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs, medical history, and current medication regimen.
2. Set a Daily Carbohydrate Limit:
Determine a target carbohydrate limit that suits your individual needs and diabetes management goals. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, a common range is typically 20-50 grams of net carbs per day. Net carbs are calculated by subtracting fiber from the total carbohydrates.
3. Choose Healthy Sources of Carbohydrates:
When consuming carbohydrates, focus on nutrient-dense, high-fiber, and low-glycemic index options. This includes non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers. These vegetables provide essential nutrients and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
4. Include Lean Proteins:
Incorporate lean sources of protein into your meals to help maintain muscle mass, promote satiety, and stabilize blood sugar levels. Good options include skinless poultry, fish, seafood, tofu, eggs, and legumes. Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid excessive calorie intake.
5. Emphasize Healthy Fats:
Healthy fats are an essential component of a low carb diet. Include foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, coconut oil, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon, sardines) in your meals. These fats provide important nutrients and contribute to satiety.
6. Minimize Refined and Processed Foods:
Avoid or minimize consumption of refined and processed foods such as white bread, pasta, rice, sugary snacks, and sugary beverages. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and should be replaced with healthier alternatives.
7. Portion Control:
Practice portion control to manage calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight. Even with a low carb diet, it’s important to be mindful of overall calorie consumption. Use measuring tools or consult a dietitian to understand appropriate portion sizes for different foods.
8. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Water has no carbohydrates or calories and can help maintain overall health and proper bodily functions. Avoid sugary drinks and opt for water, herbal tea, or unsweetened beverages.
9. Regular Monitoring:
Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to assess the impact of the low carb diet on your diabetes management. This will help you understand how different foods and portion sizes affect your blood sugar levels and allow you to make necessary adjustments.
10. Regular Follow-ups:
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional or dietitian to assess your progress, make any necessary adjustments to your diet plan, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Remember, a low carb diet is just one aspect of diabetes management. It should be combined with regular physical activity, proper medication management, stress reduction, and overall lifestyle changes for optimal results.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While a low carb diet can be highly beneficial for diabetics, it is essential to consider potential risks and make informed decisions about its implementation. Here are some important factors to keep in mind:
A. Hypoglycemia Risk and Medication Adjustments:
1. When following a low carb diet, blood sugar levels may decrease, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). It is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and work closely with healthcare professionals to adjust medication dosages accordingly.
2. Medications such as insulin or sulfonylureas that stimulate insulin secretion may need to be adjusted to prevent hypoglycemia. Close monitoring and collaboration with healthcare professionals are essential to avoid complications.
B. Nutritional Adequacy and Micronutrient Intake:
1. Restricting carbohydrate intake may affect the variety and quantity of certain nutrients obtained from food sources.
2. It is important to ensure the consumption of a wide range of nutrient-dense foods to meet the body’s requirements for vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. Incorporating non-starchy vegetables, healthy fats, and adequate protein sources can help achieve nutritional balance.
3. Consideration may be needed for specific micronutrients like vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium, which may require supplementation or careful food selection.
C. Long-Term Sustainability and Adherence:
1. A low carb diet requires a long-term commitment and may require significant changes to dietary habits. Adherence and sustainability can be challenging for some individuals.
2. It is important to find a personalized approach that suits individual preferences, lifestyle, and cultural considerations. This may involve seeking support from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians who can provide guidance and help tailor the diet to individual needs.
D. Individual Variations and Response:
1. Each person’s response to a low carb diet may vary. Some individuals may experience significant improvements in blood sugar control, while others may not see the same level of benefits.
2. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, activity levels, and metabolic differences can influence individual responses to a low carb diet. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and consultation with healthcare professionals can help track progress and make necessary adjustments.
E. Psychological Considerations:
1. Restricting certain foods, especially those high in carbohydrates, may impact an individual’s psychological well-being and relationship with food. It is important to address any emotional or psychological challenges that may arise and find strategies to maintain a positive mindset and healthy relationship with food.
2. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or therapists can be helpful in managing any psychological or emotional aspects related to dietary changes.
Navigating these potential risks and considerations requires a holistic and personalized approach. Regular communication with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians is crucial to address concerns, make necessary adjustments, and ensure the best possible outcomes for diabetes management. With the right guidance and support, a low carb diet can be an effective and sustainable strategy for improving blood sugar control and overall health.
Conclusion:
A low carb diet can be a powerful tool for diabetics to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. By reducing carbohydrate intake and focusing on nutritious whole foods, diabetics can experience improved blood sugar control, weight management, cardiovascular health, and increased energy levels. However, it is crucial to work with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized plan that meets your specific needs. Embracing a low carb lifestyle can empower diabetics to take control of their health and lead fulfilling lives despite their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: While a low carb diet can help manage and improve diabetes control, it cannot reverse the condition entirely. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that requires ongoing management. However, adopting a low carb diet can have significant benefits for diabetics, such as improved blood sugar control, reduced insulin requirements, weight management, and enhanced cardiovascular health. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes diet, medication, and regular monitoring.
A: A low carb diet can be beneficial for individuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. For type 1 diabetics, it is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to adjust insulin dosages accordingly to prevent hypoglycemia. Type 2 diabetics can benefit greatly from a low carb diet as it helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and support weight management. However, it is important to note that individual variations exist, and a personalized approach is necessary. Pregnant women, individuals with specific health conditions, or those on certain medications may require additional considerations and modifications to the diet. Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians is vital to ensure the low carb diet is suitable and safe for each individual’s unique circumstances.