Old age Diet Chart
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, including a decrease in muscle mass, changes in metabolism, and a higher risk of developing chronic diseases. A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in promoting healthy aging and maintaining overall well-being. In this blog post, we will discuss an old-age diet chart that focuses on providing the necessary nutrients to support vitality, cognitive function, and disease prevention. Let’s delve into the details and discover the key components of an optimal diet for senior citizens.
Title: The Ultimate Guide to an old age diet chart: A Pathway to Healthy Aging
Benefits of an old age diet chart
Following an old age diet chart offers numerous benefits that contribute to overall health and well-being. Let’s delve deeper into the advantages of adopting a well-planned diet during the senior years:
1. Enhances Energy Levels

A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients and calories to fuel the body and carry out daily activities. As we age, our metabolism slows down, making it important to consume nutrient-dense foods to maintain energy levels. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet can help reduce fatigue and enhance vitality, allowing you to stay active and engaged.
2. Boosts Immunity
The immune system tends to weaken with age, making older adults more susceptible to infections and diseases. Consuming a diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants strengthens the immune system, helping to ward off common illnesses. Nutrient-dense foods like citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, garlic, and yogurt can provide essential vitamins (such as vitamin C and vitamin E) and minerals (such as zinc) that support immune function and overall health.
3. Maintains Healthy Weight

Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for seniors to reduce the risk of obesity-related conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and joint problems. An old-age diet chart emphasizes portion control, balanced macronutrient distribution, and the inclusion of fiber-rich foods. Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables provide satiety and promote weight management. By following a well-regulated diet, older adults can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, enhancing their overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
4. Improves Digestion
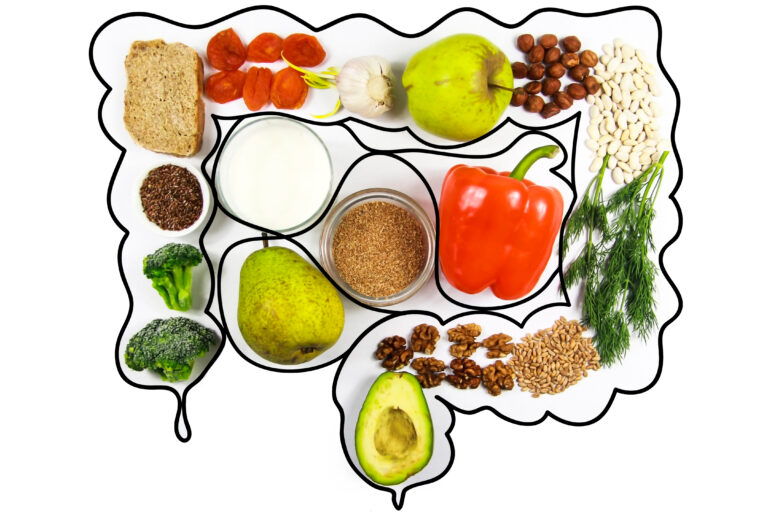

Digestive issues, such as constipation and gastrointestinal discomfort, become more common in old age. Including high-fiber foods in the diet, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, helps maintain regular bowel movements and supports digestive health. Adequate hydration is also essential for proper digestion. Drinking enough water throughout the day helps soften stools and prevent constipation, ensuring a healthy digestive system.
5. Supports Cognitive Health
Maintaining cognitive health is crucial for a fulfilling and independent lifestyle in old age. Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, have been linked to improved brain health and memory. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in fatty fish (like salmon and trout), flaxseeds, and walnuts. Antioxidants can be obtained from colorful fruits and vegetables, such as blueberries, spinach, and kale. Including these foods in an old age diet chart can help support cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Incorporating these benefits into an old age diet chart can contribute to a healthier and more vibrant life during the senior years. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to personalize the old age diet chart according to individual nutritional needs and any existing health conditions. By nourishing the body with a balanced and nutrient-rich diet, older adults can optimize their health and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Components of an old age diet chart
Creating a comprehensive old-age diet chart involves incorporating various nutrient-rich food groups to support overall health and well-being. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
1. Fruits and Vegetables

Fruits and vegetables should form the foundation of any healthy diet. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. Aim for a colorful variety to obtain a wide range of nutrients. Include leafy greens like spinach and kale, vibrant berries, citrus fruits, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower. Aim for at least five servings per day to support immune function, improve digestion, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
2. Whole Grains
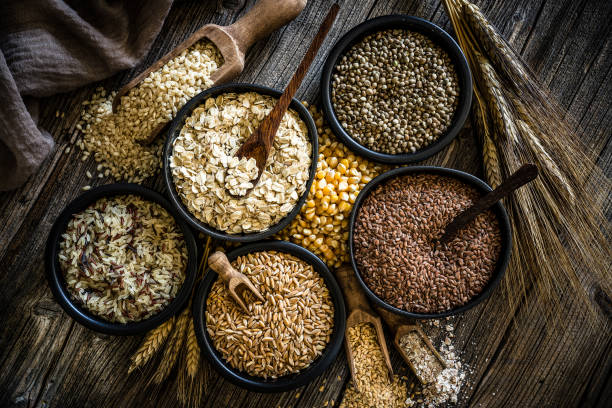

Replace refined grains with whole grains as they provide essential fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Whole grains include brown rice, whole wheat, quinoa, oats, and barley. These grains promote heart health, regulate blood sugar levels, and provide sustained energy. Incorporate whole grains into meals like whole grain bread, pasta, and cereals.
3. Protein

Protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, supporting tissue repair, and preventing muscle wasting. Include lean sources of protein in your diet such as poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products. Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and tuna, provide additional brain-boosting benefits. Plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh are excellent alternatives for vegetarians or those looking to reduce their meat intake.
4. Healthy Fats
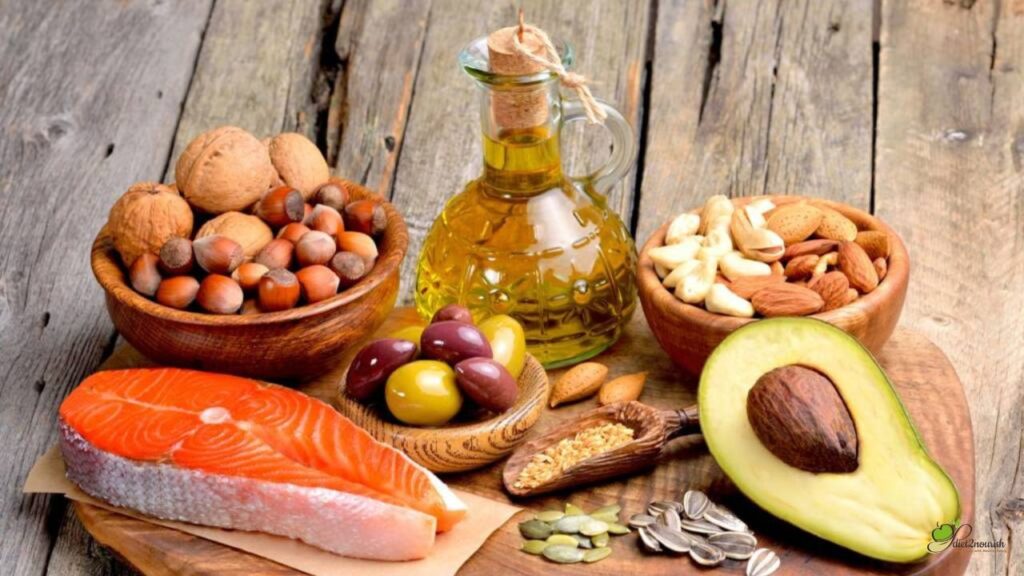

Incorporate sources of healthy fats into your diet, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are essential for brain health, heart health, and nutrient absorption. However, moderation is key as fats are calorie-dense. Opt for unsaturated fats and limit saturated and trans fats found in processed foods and fried items.
5. Dairy or Dairy Alternatives
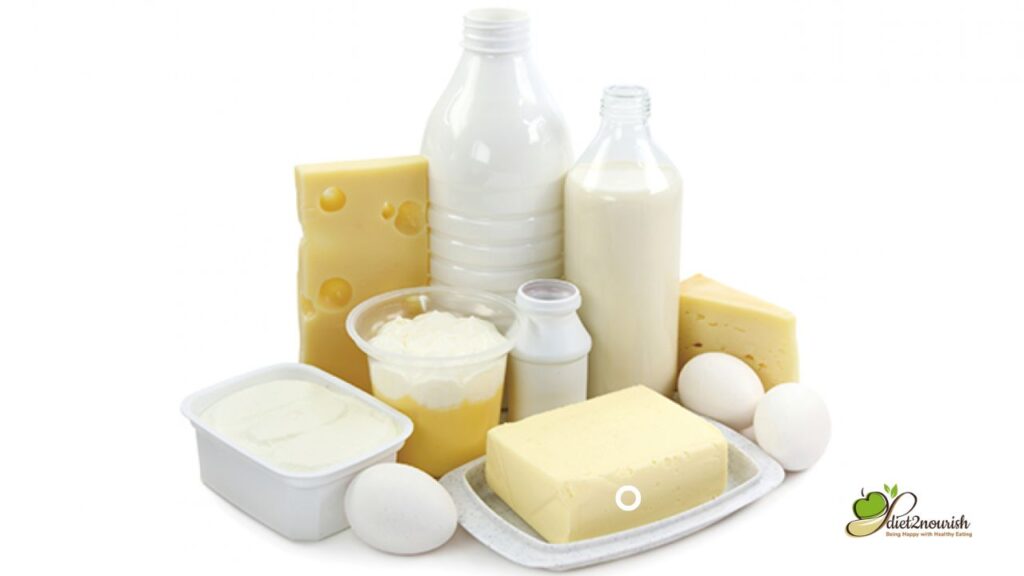

Include low-fat or non-fat dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese in your diet. These provide calcium, vitamin D, and protein, promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis. If you are lactose intolerant or prefer plant-based alternatives, opt for soy milk, almond milk, or other fortified plant-based milk substitutes.
6. Hydration
Ensure proper hydration by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Dehydration can lead to various health issues, including constipation, urinary tract infections, and cognitive impairment. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day and increase intake in hot weather or during physical activity.
7. Vitamins and Supplements
Consult a healthcare professional to determine if any specific vitamin or mineral supplements are necessary based on individual needs. Common supplements for seniors include vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Vitamin D supports bone health and immune function, while calcium helps maintain strong bones and teeth. Omega-3 fatty acids, typically found in fish oil supplements, provide anti-inflammatory benefits and support heart health.
Remember, it’s important to personalize the old age diet chart based on individual needs, preferences, and any existing health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is recommended to ensure an optimal and tailored approach to nutrition in old age.
Tips for Following an old age diet chart
In addition to incorporating nutrient-rich food groups into an old-age diet chart, there are several practical tips to follow for a healthy and balanced lifestyle:
1. Meal Planning
Planning your meals helps ensure a balanced diet and minimizes the chances of making unhealthy food choices. When creating a meal plan, aim to include a variety of colors, flavors, and textures to make meals enjoyable and satisfying. This approach ensures that you obtain a wide range of nutrients from different food sources.
2. Portion Control
Being mindful of portion sizes is important to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight. Use smaller plates and bowls to control portion sizes visually. Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid eating more than necessary.
3. Avoid Processed Foods
Minimize the consumption of processed and packaged foods as they tend to be high in salt, unhealthy fats, and added sugars. These foods often lack essential nutrients and can contribute to health issues. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible, as they provide more nutritional value.
4. Stay Active
Combining a healthy diet with regular physical activity is key to maintaining muscle strength, flexibility, and overall well-being. Engage in activities that you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, yoga, or gardening. Consult with your healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
5. Mindful Eating
Practice mindful eating by paying attention to the sensory experience of eating. Slow down, savor each bite, and chew your food thoroughly. This allows you to fully enjoy your meals and be more in tune with your body’s hunger and fullness signals. It also promotes better digestion and prevents overeating.
6. Socialize and Share Meals
Eating with friends or family can promote a positive dining experience and encourage healthier choices. Sharing meals with loved ones not only provides social interaction but also allows for better portion control and varied food options. It can be an opportunity to try new recipes or explore different cuisines together.
7. Regular Health Check-ups
Schedule regular health check-ups with your healthcare professional to monitor nutrient levels and overall health. They can help assess any nutritional deficiencies or health concerns and make necessary adjustments to your diet. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity to discuss your dietary goals and address any specific dietary needs or restrictions.
By following these practical tips in addition to incorporating an old-age diet chart, you can maintain a healthy and fulfilling lifestyle during your senior years. Remember that everyone’s nutritional needs may vary, so it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized advice based on your circumstances.
Conclusion
As we age, it is crucial to prioritize our health and well-being through proper nutrition. Following an old-age diet chart can help prevent various age-related health issues and promote healthy aging. By incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, seniors can enjoy enhanced energy levels, improved digestion, and a strengthened immune system. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is key to tailoring an old-age diet chart based on individual needs and requirements. Embrace the power of a nutritious diet and embark on a journey toward healthy aging.
Frequently Asked Question ( FAQs )
A1: The key components of an old age diet chart include incorporating nutrient-rich food groups such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control, avoiding processed foods, staying active, practicing mindful eating, socializing, and regular health check-ups are also essential for healthy aging.
A2: Following an old age diet chart promotes healthy aging by enhancing energy levels, boosting immunity, maintaining a healthy weight, improving digestion, and supporting cognitive health. The nutrient-rich foods in the diet chart provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber, while healthy lifestyle practices like staying active and socializing contribute to overall well-being. Regular health check-ups help monitor nutrient levels and ensure any necessary adjustments to the diet are made.










