How to Increase Hemoglobin Levels?
Maintaining healthy hemoglobin levels is crucial for our overall well-being. Hemoglobin, which is a protein present in red blood cells, plays a vital role in transporting oxygen throughout our bodies. When our hemoglobin levels are low, it can result in fatigue, weakness, and various health complications. If you’re aiming to naturally increase your hemoglobin levels, this blog post will offer you valuable insights and practical tips to support you on your path to optimal health.
Understanding Hemoglobin and its Importance
Hemoglobin is a vital component of our blood and plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. It is a protein found in red blood cells that binds with oxygen in the lungs and transports it to every cell and tissue in our body. This process ensures that our organs and tissues receive the oxygen they need to function properly.
The importance of hemoglobin lies in its ability to carry oxygen and remove carbon dioxide, a waste product, from the body. Without sufficient hemoglobin, our cells would be deprived of oxygen, leading to a condition known as hypoxia, which can have severe consequences for our health.
Healthy hemoglobin levels vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and altitude. For adult men, normal hemoglobin levels typically range from 13.5 to 17.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL), while for adult women, the range is usually between 12.0 and 15.5 g/dL.
When hemoglobin levels drop below the normal range, it can result in anemia. Anemia can be caused by various factors, including nutritional deficiencies (such as iron, vitamin B12, and folate), chronic diseases (such as kidney disease or cancer), and genetic disorders (such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia).
Recognizing the importance of hemoglobin and understanding the factors that can lead to low levels is crucial for maintaining our overall health and well-being. By focusing on strategies to increase hemoglobin levels naturally, we can ensure adequate oxygen supply to our cells and promote the optimal functioning of our organs and systems.
2. Causes and Symptoms of Low Hemoglobin
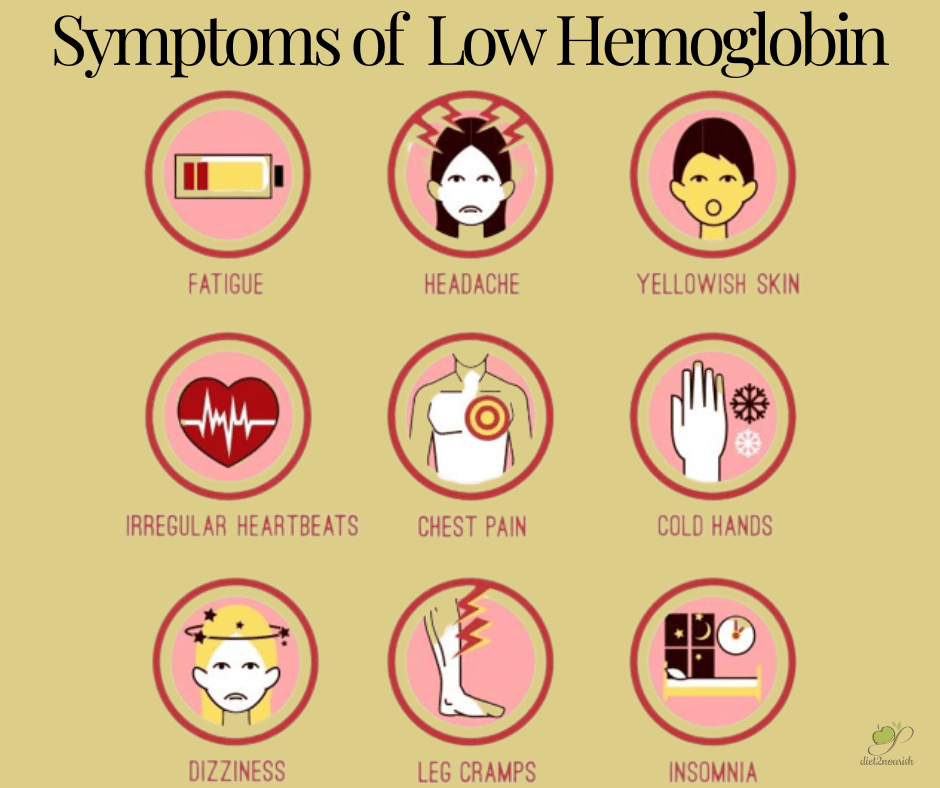
Low hemoglobin levels, also known as anemia, can have various causes and present with a range of symptoms. Understanding the causes and recognizing the symptoms of low hemoglobin is crucial for early detection and appropriate management.
There are several factors that can contribute to low hemoglobin levels. One common cause is a deficiency in essential nutrients such as iron, vitamin B12, and folate, which are necessary for red blood cell production. Inadequate intake of these nutrients through diet or poor absorption in the body can result in decreased hemoglobin levels. Another cause can be chronic diseases like kidney disease, liver disease, or certain types of cancer that affect the body’s ability to produce or maintain sufficient hemoglobin.
Certain lifestyle factors can also impact hemoglobin levels. For instance, frequent blood loss due to heavy menstruation, gastrointestinal bleeding, or ulcers can lead to anemia. Additionally, individuals following restrictive diets or those with eating disorders may not obtain enough nutrients to support proper hemoglobin production.
Recognizing the symptoms of low hemoglobin is essential for early intervention. Common symptoms include persistent fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, dizziness, and frequent headaches. Some individuals may experience rapid heartbeat, chest pain, or cold hands and feet. In severe cases, low hemoglobin can lead to complications like heart problems or delayed growth and development in children.
3. Essential Nutrients for Hemoglobin Production
To increase hemoglobin levels naturally, it is crucial to ensure an adequate intake of essential nutrients that support red blood cell production. The following subsections will explore the key nutrients necessary for hemoglobin synthesis and the foods that can help incorporate them into your diet.
Iron: The Key Mineral for Hemoglobin
Iron is a vital mineral for hemoglobin production. It is a crucial component of hemoglobin molecules and plays a central role in carrying oxygen throughout the body. Including iron-rich foods in your diet is essential for maintaining healthy hemoglobin levels. Good dietary sources of iron include lean meats, poultry, fish, dark leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Plant-based sources of iron, known as non-heme iron, can be enhanced by consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside them to improve absorption.
Vitamin C: Enhancing Iron Absorption
Vitamin C plays a significant role in enhancing the absorption of iron, particularly non-heme iron from plant-based sources. It helps convert non-heme iron into a more absorbable form, increasing its bioavailability. Including vitamin C-rich foods such as citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, kiwi, and broccoli in your meals can enhance iron absorption. Consider adding a squeeze of lemon juice to your iron-rich meals or enjoying a colorful fruit salad to boost vitamin C intake and optimize iron absorption.
Folic Acid and Vitamin B12: Vital for Red Blood Cell Formation
In addition to iron, folic acid (folate) and vitamin B12 play crucial roles in red blood cell formation and overall hemoglobin synthesis. Folic acid is necessary for DNA synthesis and cell division, while vitamin B12 is essential for the maturation of red blood cells. Good dietary sources of folic acid include leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals, and citrus fruits. Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-derived foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Including these nutrients in your diet is vital for supporting red blood cell production and maintaining healthy hemoglobin levels.
By incorporating these essential nutrients into your diet through a variety of food sources, you can support your body’s hemoglobin production and increase your overall hemoglobin levels naturally.
4. Iron-Rich Foods to Include in Your Diet
Including iron-rich foods in your diet is a key strategy to increase hemoglobin levels naturally. This section explores various food groups that are excellent sources of iron and provides insights into specific foods within each group.
Dark Leafy Greens: Spinach, Kale, and Swiss Chard
Dark leafy greens are nutritional powerhouses and excellent sources of non-heme iron. Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and other greens are not only rich in iron but also packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These greens can be enjoyed in salads, stir-fries, smoothies, or as a side dish, providing a nutrient boost to your meals while supporting healthy hemoglobin levels.
Legumes: Lentils, Chickpeas, and Beans
Legumes, including lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans, are plant-based sources of iron and other essential nutrients. They are not only rich in iron but also high in protein and fiber, making them a nutritious addition to your diet. Incorporate legumes into soups, stews, salads, or as a side dish to increase your iron intake and support hemoglobin production.
Lean Meats and Poultry
Lean meats and poultry are excellent sources of heme iron, which is highly absorbable by the body. Chicken, turkey, lean beef, and pork are examples of iron-rich animal-derived foods. When choosing meats, opt for lean cuts and healthy cooking methods such as grilling, baking, or broiling to maintain their nutritional value. Including moderate portions of lean meats and poultry in your diet can provide a significant amount of heme iron to support healthy hemoglobin levels.
Seafood: Shellfish and Fish
Seafood, particularly shellfish, and fish, offer a good amount of iron along with other essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids. Examples of iron-rich seafood include clams, oysters, mussels, sardines, and salmon. These options not only contribute to your iron intake but also provide health benefits for your cardiovascular system and brain. Incorporate seafood into your diet by enjoying grilled fish fillets, seafood stir-fries, or adding shellfish to pasta dishes, and support your hemoglobin levels while diversifying your menu.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, Pumpkin Seeds, and Quinoa
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and sesame seeds, are nutrient-dense foods that contain iron. They can be enjoyed as snacks, added to salads, or used as toppings for various dishes. Additionally, quinoa, a pseudo-grain, is a good source of iron and can be used as a base for salads, side dishes, or even as a breakfast cereal. Incorporating these nuts, seeds, and grains into your meals and snacks can contribute to your iron intake and support healthy hemoglobin levels.
5. Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Hemoglobin Levels
In addition to incorporating iron-rich foods and essential nutrients into your diet, certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to enhancing hemoglobin levels naturally. This section explores key lifestyle factors that can support healthy hemoglobin production.
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity can have a positive impact on hemoglobin levels. Exercise stimulates the production of red blood cells, which in turn supports hemoglobin synthesis. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing are excellent choices. Remember to start gradually and consult with your healthcare professional before beginning any new exercise program, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Managing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can adversely affect hemoglobin levels and overall health. High levels of stress can disrupt hormonal balance and impair red blood cell production. Implementing stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities you enjoy can help reduce stress levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress and create a balanced lifestyle, which can positively influence hemoglobin production.
5 foods to increase Hemoglobin

Increasing hemoglobin levels can be achieved by consuming foods rich in iron, vitamin C, and other nutrients that support the production of red blood cells. Here are five foods that can help increase hemoglobin levels:
Spinach
Spinach is a powerhouse of iron and other essential vitamins and minerals. It provides a good dose of non-heme iron, which is important for boosting hemoglobin levels. It is also rich in vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption.
Lentils
Lentils are a great source of plant-based protein and iron. They are also high in folate and vitamin B6, which aid in red blood cell production. Incorporating lentils into your diet can effectively increase hemoglobin levels.
Beetroot
Beetroot is rich in iron, folic acid, and antioxidants. The iron content in beetroot stimulates the production of hemoglobin, while the antioxidants help in maintaining the overall health of red blood cells.
Pomegranate
Pomegranate is a fruit packed with iron, vitamin C, and antioxidants. It promotes the production of healthy red blood cells and improves overall blood circulation. Drinking pomegranate juice or including the fruit in your diet can be beneficial.
Lean meats
Animal sources such as lean meats, including beef, chicken, and turkey, are rich in heme iron, which is highly absorbable by the body. Heme iron aids in the production of hemoglobin and is particularly beneficial for individuals with low hemoglobin levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy hemoglobin levels is crucial for our overall well-being. Hemoglobin plays a vital role in carrying oxygen throughout the body, and low levels can lead to fatigue, weakness, and various health complications. By understanding the importance of hemoglobin and the factors that contribute to low levels, we can take proactive steps to increase hemoglobin naturally.
Incorporating iron-rich foods, such as dark leafy greens, legumes, lean meats, seafood, and nuts and seeds, into our diet provides essential nutrients for hemoglobin production. Additionally, ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin C, folic acid, and vitamin B12 supports red blood cell formation. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient rest and sleep further enhances hemoglobin levels.
By combining these strategies and seeking professional guidance when necessary, we can optimize our hemoglobin levels and promote optimal health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to monitor your progress. With dedication and conscious efforts, you can embark on a journey to improve your hemoglobin levels and enjoy the benefits of optimal health and vitality.
Frequently Ask Questions
A: Absolutely! Our comprehensive guide provides various natural methods to increase hemoglobin levels. It includes dietary recommendations, lifestyle changes, and tips to incorporate iron-rich foods and vitamin C sources into your meals. By following these natural approaches, you can boost your hemoglobin levels without relying solely on supplements.
A: Yes, certain foods are particularly beneficial for increasing hemoglobin levels. Our guide highlights iron-rich foods such as spinach, lentils, and lean meats, which provide essential nutrients for hemoglobin production. Additionally, we explore the benefits of consuming foods rich in vitamin C, like citrus fruits and pomegranates, as they enhance iron absorption. These dietary recommendations can effectively support your body’s natural hemoglobin production process.









